What is OCR full form in Banking?
OCR is the process of using technology to read characters from printed or handwritten text included inside digital images of actual documents, such scanned paper documents (optical character recognition). OCR’s primary function is to read a document’s text and convert the characters into code that may be used for data processing. Another name for optical character recognition is text recognition (OCR).
To convert physical documents into text that can be read by machines, OCR systems use a combination of hardware and software. Hardware, such an optical scanner or specialised circuit board, is used to copy or read text, while software often handles complex processing.
The programme can also use artificial intelligence (AI) to achieve more complex techniques of intelligent character recognition (ICR), such as recognising languages or handwriting styles.
OCR is most typically used to convert hard-copy legal or historical documents into PDFs. Users may modify, format, and search the document in this soft copy as if it were generated with a word processor.
Digital Onboarding is great use of OCR tools, to extract and verify documents and IDs with automated solutions that use AI to perform authentications of various fields such as name, address, ID number, etc.

How Optical Character Recognition – OCR works
Processing a document’s physical form with a scanner is the first step in OCR. OCR software converts the document to a two-color, or black and white, form after copying all of the pages. Dark areas of the scanned-in image or bitmap indicate characters that must be recognised, while light areas denote background. These areas are examined for light and dark regions.
The dark areas are then subjected to further analysis to search for alphabetic or numerical digits. Many strategies are used by OCR algorithms, but the majority concentrate on one letter, phrase, or block of text at a time. Character detection then occurs using one of two algorithms:
Pattern recognition. Text samples in various fonts and formats are provided to OCR programmes, which are then compared and recognised on the scanned page.
Feature detection. OCR programmes utilise rules based on the attributes of a particular letter or number to recognise characters in a scanned page. For example, a character’s characteristics might include the number of angled lines, crossed lines, or curves. For example, the capital letter “A” might be represented by two diagonal lines crossed in the centre by a horizontal line.
When a character is identified, it is converted into an ASCII code that computers may use to do additional actions. Users should correct basic errors, proofread, and double-check intricate layouts before storing the document for future use.
What are the key processes in Optical Character Recognition – OCR?
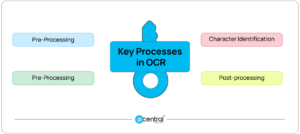
- Pre-Processing: Character Identification, and Post-Processing are the three main ideas that underpin OCR.
- Pre-Processing: OCR ensures that the scanned document or picture is optimised before the all-important Machine Learning algorithms come in with their character recognition and text identification abilities. This stage improves recognition accuracy by removing faults, improving the picture, and removing distortions.
- Character Identification: The initial step in this procedure is to define the data set that will be extracted. This is known as ‘Feature Extraction,’ a procedure that rejects undesired information and extracts only important data before transforming it into machine-readable text using ML and Deep Learning engines.
- Post-processing: Post-processing is used to improve accuracy and rectify mistakes. A lexicon is used to protect many OCR applications. This causes the algorithm to validate and cross-reference the output of a list of bespoke phrases created for a specific industry or application.
What are the applications for Optical Character Recognition (OCR)?
OCR may be used for a number of purposes, including the following:
- Scanning printed papers and converting them into editable formats for word processors such as Microsoft Word or Google Docs.
- Print material is being indexed for search engines.
- Data entry, extraction, and processing are all being automated.
- Deciphering documents into text that visually impaired or blind persons can read aloud.
- Keeping historical documents in searchable formats, such as newspapers, magazines, or phonebooks.
- Computerized check depositing eliminates the need for a bank teller.
- Inserting vital, signed legal papers into an electronic database.
- Using a camera or software to recognise text, such as licence plates.
- Sorting letters in preparation for postal delivery.
- Words within a picture are translated into a specific language.
What are the benefits of Optical Character Recognition – OCR?
The major benefits of OCR technology are that it saves time, reduces mistakes, reduces effort, and enables operations that physical copies do not allow, such as compressing into ZIP files, highlighting keywords, incorporating into a website, and attaching to an email.
Although capturing photographs of papers allows them to be digitally saved, OCR adds the ability to alter and search those materials.
OCR in Banking
The process of turning scanned documents and image-based information such as handwritten, typed, or printed text into a digital, machine-readable text format is known as optical character recognition (OCR). The whole OCR technique revolves around transforming analogue text into digital text, or a format that can be encoded by a computer. OCR is a simple yet successful technology that leverages a simple notion to produce outcomes with vast industrial applications, saving businesses millions of dollars and man-hours.
Why is Optical Character Recognition – OCR important in Banking?
OCR is a genuinely game-changing invention. OCR’s numerous uses and functions cannot be emphasised. Document Extraction digitises everything, from official papers like passports to licence plate identification. Even smartphone apps make use of OCR by assisting individuals with routine day-to-day chores. Applications that convert tourist signage in other languages to your own language while on vacation abroad are an excellent illustration of how OCR has been revolutionary not only for companies and governments, but also for the general public.
The benefits of OCR are just endless, and one could go on and on about them. Yet, one business in particular stands to benefit the most from this technology, and that is BANKING.
What are the Optical Character Recognition – OCR Applications in Banking?
Ever notice how, only a few years ago, even simple bank transactions took at least 5 to 7 business days, but now everything is instant? OCR, on the other hand, has played a critical part in making things lightning quick. AI enabled Document Extraction, along with other digital technologies, opened the path for contemporary banking, for which we are eternally grateful.
Today’s 25-35 age group, who regarded conventional banking as a tiresome, time-consuming, and excruciating procedure when accompanying their parents to a bank as children, can now perform marvels with only a few clicks on their cellphones.
Manual backlogs and mountains of paper-based transactions slowed things down before OCR. As a result, resources were kept occupied while the bank lost important hours completing routine activities such as cashing a check or processing a bank statement.
Optical Character Recognition – OCR Banking In 2023
In 2023, you no longer need a particularly trained individual to enter information from a cheque into a digital system. OCR can scan a check from top to bottom and identify distinct portions such as the serial code, the person’s account number, the IFSC code, the amount submitted, and the signature. After detecting these parts, it will automatically enter the data into their assigned column in the bank’s system’s designated account. The best thing is that all of this will occur before you can even read this phrase. Yet, before we go into the uses of OCR in the banking business, let us first comprehend the basic premise of this technology.
If banking moves quickly, the entire world moves quicker, and the simple combination of these three fundamental concepts contributes significantly to the acceleration of financial activities worldwide.
IDcentral’s OCR based Document Verification solution
IDcentral’s Document Verification solution based on an API based platform helps in user onboarding and identity verification in many ways. By using AI-enabled OCR, document verification now helps with:
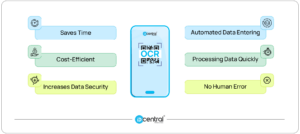
- Manual data entering is automated.
- Processing data more quickly
- Not susceptible to human error
- Cloud storage facilitates data collaboration, which boosts productivity and saves time.
- Cost-efficient
- Increases data security and stability.
Companies are searching for simple verification solutions. As previously stated, IDcentral’s OCR technology significantly decreases verification time and direct input from the end-user, which is otherwise highly scary because who enjoys filling out lengthy forms?? Nobody!
All your consumers have to do is scan a photo of their national ID and they’re ready to go!!
Try IDcentral’s AI enabled Document Extraction solution – DeepScanRequest a demo

Sumanth Kumar is a Marketing Associate at IDcentral. With hands-on experience with all of IDcentral’s KYC and Onboarding Technology, he loves to create indispensable digital content about the trends in User Onboarding across multiple industries.

